AS and IP prefix
Writing IYP queries from scratch is daunting!.. But once you can read queries, you can easily modify them, and get the data you are looking for.
In the following, we conduct small studies using IYP and provide all corresponding queries. This should give you enough material to start writing your own queries. Execute these examples in the IYP console, then try tuning or combining some of the queries. Also remember to click on the database icon (top left corner in the IYP console) to see all node and relationship types and get examples by clicking on any of those.
First, we will learn about queries for finding specific prefixes and ASes. We also use these examples to explain how to use the IYP console interface and provide some tricks for making your own queries.
Find prefixes originated by an AS
We start by looking at the prefixes originated by a certain AS which is
represented in IYP by the ORIGINATE relationship between AS and Prefix
nodes.
Here is the query to find prefixes originated by AS2497:
MATCH p = (:AS {asn:2497})-[:ORIGINATE]-(:Prefix)
RETURN p
Copy/paste this query into the IYP Console. You should obtain a busy graph like this:
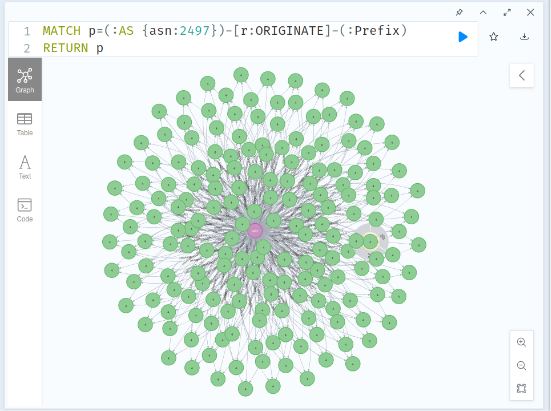
By clicking on any of the nodes you will see its properties in the right
sidepanel (if you do not see the panel, click the < icon).
It should look something like this:
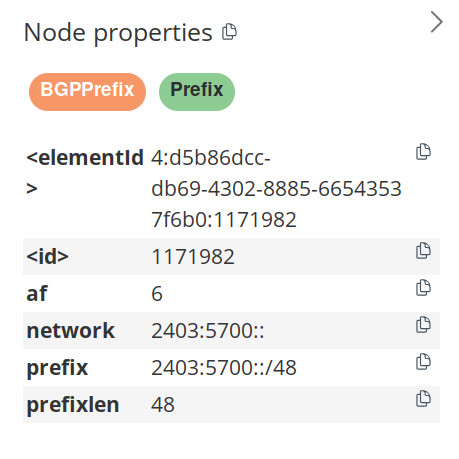
Here you can see that the nodes can have multiple types.
This node has the generic Prefix type and the more specific BGPPrefix node
type.
To be more precise we can use the type BGPPrefix in our query.
Also, the af property (i.e., Address Family) tells us if the prefix is for
IPv4 or IPv6.
So to find all IPv6 prefixes originated by AS2497 we can filter prefixes using
the af property:
MATCH p = (:AS {asn:2497})-[:ORIGINATE]-(:BGPPrefix {af: 6})
RETURN p
Copy/paste this query into the IYP Console, you should obtain another cute graph.
You may wonder why there are multiple links between the same pair of nodes.
This is because multiple datasets provide us with this same information.
Clicking on the links you can see that the reference_org property is
different.
Some are from BGPKIT, some are from Packet Clearing House and some are from IHR.
IYP gives you the possibility to filter per dataset.
If you want to query only data from BGPKIT, you can filter on this property, or
even better on the reference_name property which is a unique name for the
dataset:
MATCH p = (:AS {asn:2497})-[r:ORIGINATE]-(:BGPPrefix {af: 6})
WHERE r.reference_name = 'bgpkit.pfx2asn'
RETURN p
For analysis we need the actual list of prefixes (not a cute graph). To do that we can ask Cypher to return property values instead of nodes and relationships. The following query returns a list of IPv6 prefixes originated by AS2497:
MATCH (:AS {asn:2497})-[:ORIGINATE]-(pfx:BGPPrefix {af: 6})
RETURN DISTINCT pfx.prefix
Note the use of the keyword DISTINCT in the RETURN statement.
This ensures that we retrieve only unique rows.
Since we have multiple links that match this pattern, the query would have
returned multiple times the same prefix (try the query without DISTINCT).
Executing the above query you should see a table listing all prefixes:
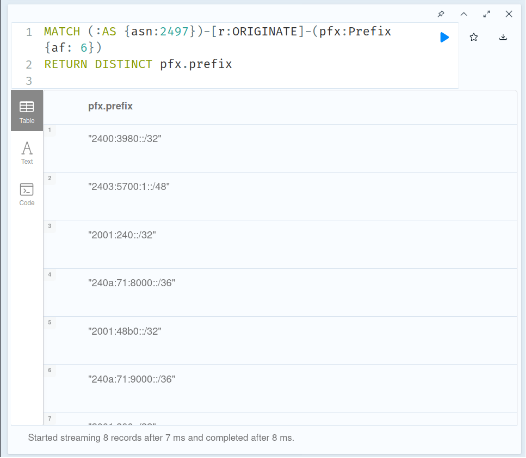
You can download the data in CSV or JSON format via the download icon at the top right corner.
Finally, we can also search for more complex patterns in the graph.
The following query looks for prefixes that are originated by two different
origin ASes.
The return values are the prefix, the two origin ASes, and the count values
provided by BGPKIT (the number of RIS and RouteViews peers that see the
prefix/origin pair).
MATCH (a:AS)-[ra:ORIGINATE {reference_name: 'bgpkit.pfx2asn'}]-(pfx:BGPPrefix)-[rb:ORIGINATE {reference_name: 'bgpkit.pfx2asn'}]-(b:AS)
WHERE a <> b
RETURN DISTINCT pfx.prefix, a.asn, b.asn, ra.count, rb.count
LIMIT 100
As we write more complex Cypher queries the searched pattern may become very
long and hard to read.
In this case we can also use multiple MATCH clauses.
The following query gives the exact same results as the previous one:
MATCH (a:AS)-[ra:ORIGINATE {reference_name: 'bgpkit.pfx2asn'}]-(pfx:BGPPrefix)
MATCH (pfx)-[rb:ORIGINATE {reference_name: 'bgpkit.pfx2asn'}]-(b:AS)
WHERE a <> b
RETURN DISTINCT pfx.prefix, a.asn, b.asn, ra.count, rb.count
LIMIT 100
Exercises
- Write a query that fetches only IPv4 prefixes.
- Write a query that fetches only /24 prefixes.
ORIGINATEis not the only type of relationship betweenASandPrefixnodes. For example, for RPKI we have theROUTE_ORIGIN_AUTHORIZATIONrelationship betweenASandPrefixnodes. Find prefixes that are announced by one AS and that have a ROA for another AS.